Autogenerate MCP tools from a RESTful API
Use the AI MCP Proxy to map your REST API endpoints into MCP capabilities, allowing you to integrate them directly with AI Gateway.
Prerequisites
Kong Konnect
This is a Konnect tutorial and requires a Konnect personal access token.
-
Create a new personal access token by opening the Konnect PAT page and selecting Generate Token.
-
Export your token to an environment variable:
export KONNECT_TOKEN='YOUR_KONNECT_PAT'Copied! -
Run the quickstart script to automatically provision a Control Plane and Data Plane, and configure your environment:
curl -Ls https://get.konghq.com/quickstart | bash -s -- -k $KONNECT_TOKEN -e KONG_STATUS_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8100 --deck-outputCopied!This sets up a Konnect Control Plane named
quickstart, provisions a local Data Plane, and prints out the following environment variable exports:export DECK_KONNECT_TOKEN=$KONNECT_TOKEN export DECK_KONNECT_CONTROL_PLANE_NAME=quickstart export KONNECT_CONTROL_PLANE_URL=https://us.api.konghq.com export KONNECT_PROXY_URL='http://localhost:8000'Copied!Copy and paste these into your terminal to configure your session.
Kong Gateway running
This tutorial requires Kong Gateway Enterprise. If you don’t have Kong Gateway set up yet, you can use the quickstart script with an enterprise license to get an instance of Kong Gateway running almost instantly.
-
Export your license to an environment variable:
export KONG_LICENSE_DATA='LICENSE-CONTENTS-GO-HERE'Copied! -
Run the quickstart script:
curl -Ls https://get.konghq.com/quickstart | bash -s -- -e KONG_LICENSE_DATACopied!Once Kong Gateway is ready, you will see the following message:
Kong Gateway Ready
decK v1.43+
decK is a CLI tool for managing Kong Gateway declaratively with state files. To complete this tutorial, install decK version 1.43 or later.
This guide uses deck gateway apply, which directly applies entity configuration to your Gateway instance.
We recommend upgrading your decK installation to take advantage of this tool.
You can check your current decK version with deck version.
Required entities
For this tutorial, you’ll need Kong Gateway entities, like Gateway Services and Routes, pre-configured. These entities are essential for Kong Gateway to function but installing them isn’t the focus of this guide. Follow these steps to pre-configure them:
-
Run the following command:
echo ' _format_version: "3.0" services: - name: mcp-service url: http://host.docker.internal:3000 routes: - name: mcp-route paths: - "/marketplace" service: name: mcp-service ' | deck gateway apply -Copied!
To learn more about entities, you can read our entities documentation.
Cursor
This tutorial uses Cursor as an MCP client:
- Go to the Cursor downloads page.
- Download the installer for your operating system.
- Install Cursor on your machine.
- Launch Cursor and sign in to your account or create a new account.
Install mock API Server
Before using the AI MCP Proxy plugin, you’ll need an upstream HTTP API to expose. For this tutorial, we’ll use a simple mock API built with Express. This allows you to test the plugin without relying on an external service. This mock API simulates a small marketplace system with a fixed set of users and their associated orders. Each user has between two and five sample orders, which the API exposes through /marketplace/users and /marketplace/{userId}/orders endpoints.
Running these commands will download the mock API script and install any required dependencies automatically:
curl -s -o api.js "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/subnetmarco/5ddb23876f9ce7165df17f9216f75cce/raw/a44a947d69e6f597465050cc595b6abf4db2fbea/api.js"
npm install express
node api.js
Validate the API is running:
curl -X GET http://localhost:3000
This request confirms that the mock server is up and responding. Later, the AI MCP Proxy will use this API’s OpenAPI schema to generate MCP tool definitions. You should see the following response from the server:
{"name":"Sample Users API"}%
Configure the AI MCP Proxy plugin
With the mock API server running, configure the AI MCP Proxy plugin to expose its endpoints as MCP tools. The following example maps the mock API operations to MCP tool definitions that the client can invoke.
echo '
_format_version: "3.0"
plugins:
- name: ai-mcp-proxy
route: mcp-route
config:
mode: conversion-listener
tools:
- description: Get users
method: GET
path: "/marketplace/users"
parameters:
- name: id
in: query
required: false
schema:
type: string
description: Optional user ID
- description: Get orders for a user
method: GET
path: "/marketplace/orders"
parameters:
- description: User ID to filter orders
in: query
name: userid
required: true
schema:
type: string
server:
timeout: 60000
' | deck gateway apply -
-
Open your Cursor desktop app.
-
Navigate to Settings in the top right corner.
-
In the Cursor Settings tab, go to Tools & MCP in the left sidebar.
-
In the Installed MCP Servers section, click New MCP Server.
-
Paste the following JSON configuration into the newly opened
mcp.jsontab:{ "mcpServers": { "marketplace": { "url": "http://localhost:8000/marketplace" } } }Copied! -
Return to the Cursor settings tab. You should now see the weather MCP server with one tool available:
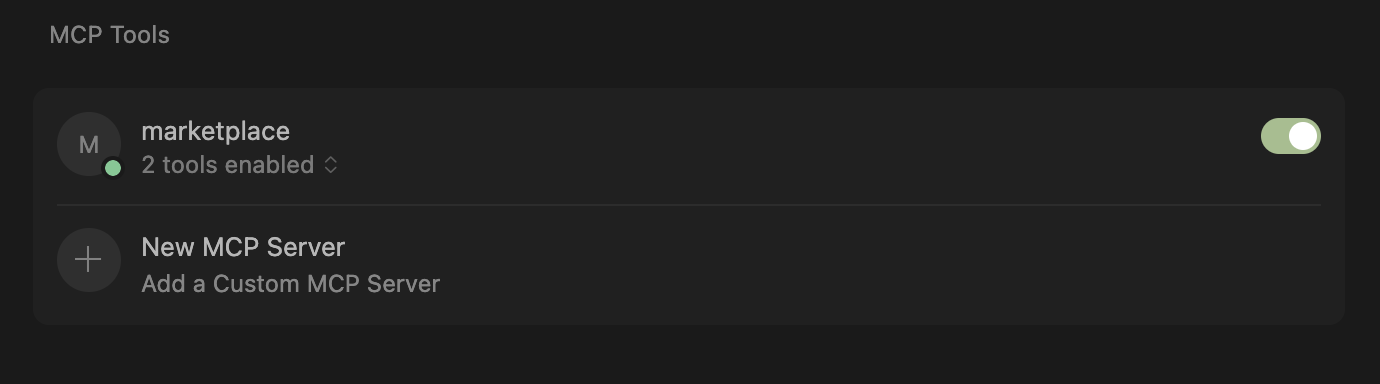
-
To open a new Cursor chat, click cmd + L if you’re on Mac, or ctrl + L if you’re on Windows.
-
In the Cursor chat tab, click @ Add Context and select
mcp.json:
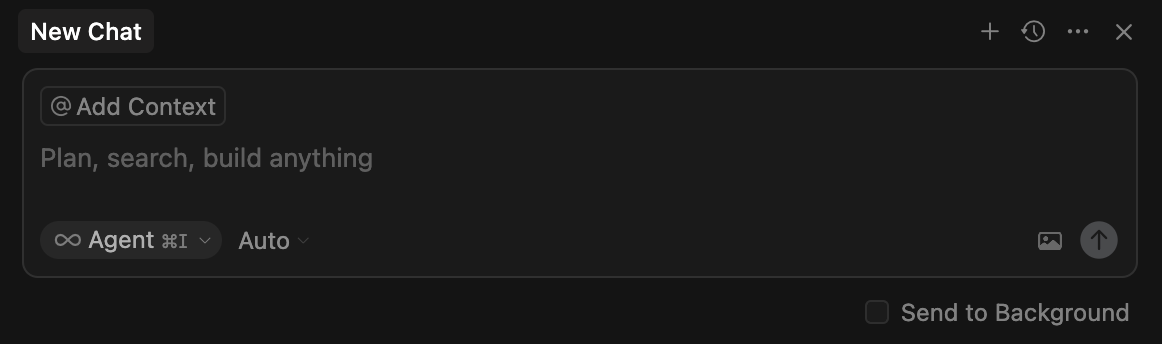
Validate the configuration
Enter the following question in the Cursor chat:
What users do you see in the API?
I'll query the marketplace service for the list of users
> Called mcp-route-1
When the agent finishes reasoning, You should see the following output:
Let me check what users are available in the API:
I can see 10 users in the API:
1. Alice Johnson (ID: a1b2c3d4)
2. Bob Smith (ID: e5f6g7h8)
3. Charlie Lee (ID: i9j0k1l2)
4. Diana Evans (ID: m3n4o5p6)
5. Ethan Brown (ID: q7r8s9t0)
6. Fiona Clark (ID: u1v2w3x4)
7. George Harris (ID: y5z6a7b8)
8. Hannah Lewis (ID: c9d0e1f2)
9. Ian Walker (ID: g3h4i5j6)
10. Julia Turner (ID: k7l8m9n0)
Now, we can check what Alice Johnson ordered by entering the following message in the Cursor chat:
What did Alice Johnson order?
You’ll notice that Cursor calls the tools exposed by the AI MCP Proxy plugin:
I'll look up the list of users to find Alice's user ID. Then I'll fetch her orders.
> called mcp-route-1
> called mcp-route-2
When the agent finishes reasoning, you should see the following response:
Sugar (50kg)
Cleaning Supplies Pack
Canned Tomatoes (100 cans)
You can validate this result against the API exposed in the previous step.