Visualize LLM traffic with Prometheus and Grafana
Enable the AI Proxy Advanced plugin to collect detailed request and model statistics. Then configure the Prometheus plugin to expose these metrics for scraping. Finally, connect Grafana to visualize model performance, usage trends, and traffic distribution in real time.
Prerequisites
Kong Konnect
This is a Konnect tutorial and requires a Konnect personal access token.
-
Create a new personal access token by opening the Konnect PAT page and selecting Generate Token.
-
Export your token to an environment variable:
export KONNECT_TOKEN='YOUR_KONNECT_PAT'Copied! -
Run the quickstart script to automatically provision a Control Plane and Data Plane, and configure your environment:
curl -Ls https://get.konghq.com/quickstart | bash -s -- -k $KONNECT_TOKEN -e KONG_STATUS_LISTEN=0.0.0.0:8100 --deck-outputCopied!This sets up a Konnect Control Plane named
quickstart, provisions a local Data Plane, and prints out the following environment variable exports:export DECK_KONNECT_TOKEN=$KONNECT_TOKEN export DECK_KONNECT_CONTROL_PLANE_NAME=quickstart export KONNECT_CONTROL_PLANE_URL=https://us.api.konghq.com export KONNECT_PROXY_URL='http://localhost:8000'Copied!Copy and paste these into your terminal to configure your session.
Kong Gateway running
This tutorial requires Kong Gateway Enterprise. If you don’t have Kong Gateway set up yet, you can use the quickstart script with an enterprise license to get an instance of Kong Gateway running almost instantly.
-
Export your license to an environment variable:
export KONG_LICENSE_DATA='LICENSE-CONTENTS-GO-HERE'Copied! -
Run the quickstart script:
curl -Ls https://get.konghq.com/quickstart | bash -s -- -e KONG_LICENSE_DATACopied!Once Kong Gateway is ready, you will see the following message:
Kong Gateway Ready
decK v1.43+
decK is a CLI tool for managing Kong Gateway declaratively with state files. To complete this tutorial, install decK version 1.43 or later.
This guide uses deck gateway apply, which directly applies entity configuration to your Gateway instance.
We recommend upgrading your decK installation to take advantage of this tool.
You can check your current decK version with deck version.
Required entities
For this tutorial, you’ll need Kong Gateway entities, like Gateway Services and Routes, pre-configured. These entities are essential for Kong Gateway to function but installing them isn’t the focus of this guide. Follow these steps to pre-configure them:
-
Run the following command:
echo ' _format_version: "3.0" services: - name: example-service url: http://httpbin.konghq.com/anything routes: - name: example-route paths: - "/anything" service: name: example-service ' | deck gateway apply -Copied!
To learn more about entities, you can read our entities documentation.
OpenAI
This tutorial uses OpenAI:
- Create an OpenAI account.
- Get an API key.
-
Create a decK variable with the API key:
export DECK_OPENAI_API_KEY='YOUR OPENAI API KEY'Copied!
Mistral
This tutorial uses Mistral:
- Create a Mistral account.
- Get your API key.
- Export a decK environment variable with the Mistral API key:
export DECK_MISTRAL_API_KEY='YOUR MISTRAL API KEY'
Grafana
Ensure Grafana is installed locally and accessible. You can quickly start a Grafana instance using Docker:
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name=grafana grafana/grafana-enterprise
This command pulls the official Grafana Enterprise image and runs it on port 3000. Once running, Grafana is accessible at http://localhost:3000.
On first login, use the default credentials:
-
Username:
admin -
Password:
admin
Grafana will prompt you to set a new password after the initial login.
Configure the AI Proxy Advanced plugin
To expose AI traffic metrics to Prometheus, you must first configure the AI Proxy Advanced plugin to enable detailed logging. This makes request payloads, model performance statistics, and cost metrics available for collection.
In this example, traffic is balanced between OpenAI’s gpt-4.1 and Mistral’s mistral-tiny models using a round-robin algorithm. For each model target, logging is enabled to capture request counts, latencies, token usage, and payload data. Additionally, we define input_cost and output_cost values to track estimated usage costs per 1,000 tokens, which are exposed as Prometheus metrics.
Apply the following configuration to enable metrics collection for both models:
echo '
_format_version: "3.0"
plugins:
- name: ai-proxy-advanced
config:
balancer:
algorithm: round-robin
targets:
- model:
provider: openai
name: gpt-4.1
options:
max_tokens: 512
temperature: 1.0
input_cost: 0.75
output_cost: 0.75
route_type: llm/v1/chat
logging:
log_payloads: true
log_statistics: true
auth:
header_name: Authorization
header_value: Bearer ${{ env "DECK_OPENAI_API_KEY" }}
weight: 50
- model:
provider: mistral
name: mistral-tiny
options:
mistral_format: openai
upstream_url: https://api.mistral.ai/v1/chat/completions
input_cost: 0.25
output_cost: 0.25
route_type: llm/v1/chat
logging:
log_payloads: true
log_statistics: true
auth:
header_name: Authorization
header_value: Bearer ${{ env "DECK_MISTRAL_API_KEY" }}
weight: 50
' | deck gateway apply -
Enable the Prometheus plugin
Before you configure Prometheus, enable the Prometheus plugin on Kong Gateway. In this example, we’ve enabled two types of metrics: status code metrics, and AI metrics which expose detailed performance and usage data for AI-related requests.
echo '
_format_version: "3.0"
plugins:
- name: prometheus
config:
status_code_metrics: true
ai_metrics: true
bandwidth_metrics: true
latency_metrics: true
upstream_health_metrics: true
' | deck gateway apply -
Configure Prometheus
Create a prometheus.yml file:
touch prometheus.yml
Now, add the following to the prometheus.yml file to configure Prometheus to scrape Kong Gateway metrics:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kong'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['kong-quickstart-gateway:8001']
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kong'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['kong-quickstart-gateway:8100']
Now, run a Prometheus server, and pass it the configuration file created in the previous step:
docker run -d --name kong-quickstart-prometheus \
--network=kong-quickstart-net -p 9090:9090 \
-v $(PWD)/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
prom/prometheus:latest
Prometheus will begin to scrape metrics data from AI Gateway.
Configure Grafana dashboard
Add Prometheus data source
- In the Grafana UI, go to Connections > Data Sources. If you’re using the Grafana setup from the prerequisites, you can access the UI at http://localhost:3000/.
- Click Add data source.
- Select Prometheus from the list.
- In the Prometheus server URL field, enter:
http://host.docker.internal:9090. - Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Save & test to verify the connection. If successful, you’ll see the following message:
Successfully queried the Prometheus API.Copied!
Import Dashboard
- In the Grafana UI, navigate to Dashboards.
- Select “Import” from the New dropdown menu.
- Enter
21162in the Find and import dashboards for common applications field. - Click Load.
- In the Prometheus dropdown, select the Prometheus data source you created previously.
- Click Import.
View Grafana configuration
Now, we can generate traffic by running the following CURL request:
for i in {1..5}; do
echo -n "Request #$i — Model: "
curl -s -X POST "http://localhost:8000/anything" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello!"
}
]
}' | jq -r '.model'
sleep 10
done
Once it’s finished, you’ll see something like the following in the output. Notice that the requests were routed to different models based on the load balancing you configured earlier:
Request #1 — Model: gpt-4.1-2025-04-14
Request #2 — Model: mistral-tiny
Request #3 — Model: mistral-tiny
Request #4 — Model: mistral-tiny
Request #5 — Model: gpt-4.1-2025-04-14
View metrics in Grafana
Now you can visualize that traffic in the Grafana dashboard.
- Open Grafana in your browser at http://localhost:3000.
- Navigate to Dashboards in the sidebar.
- Click the Kong CX AI dashboard you imported earlier.
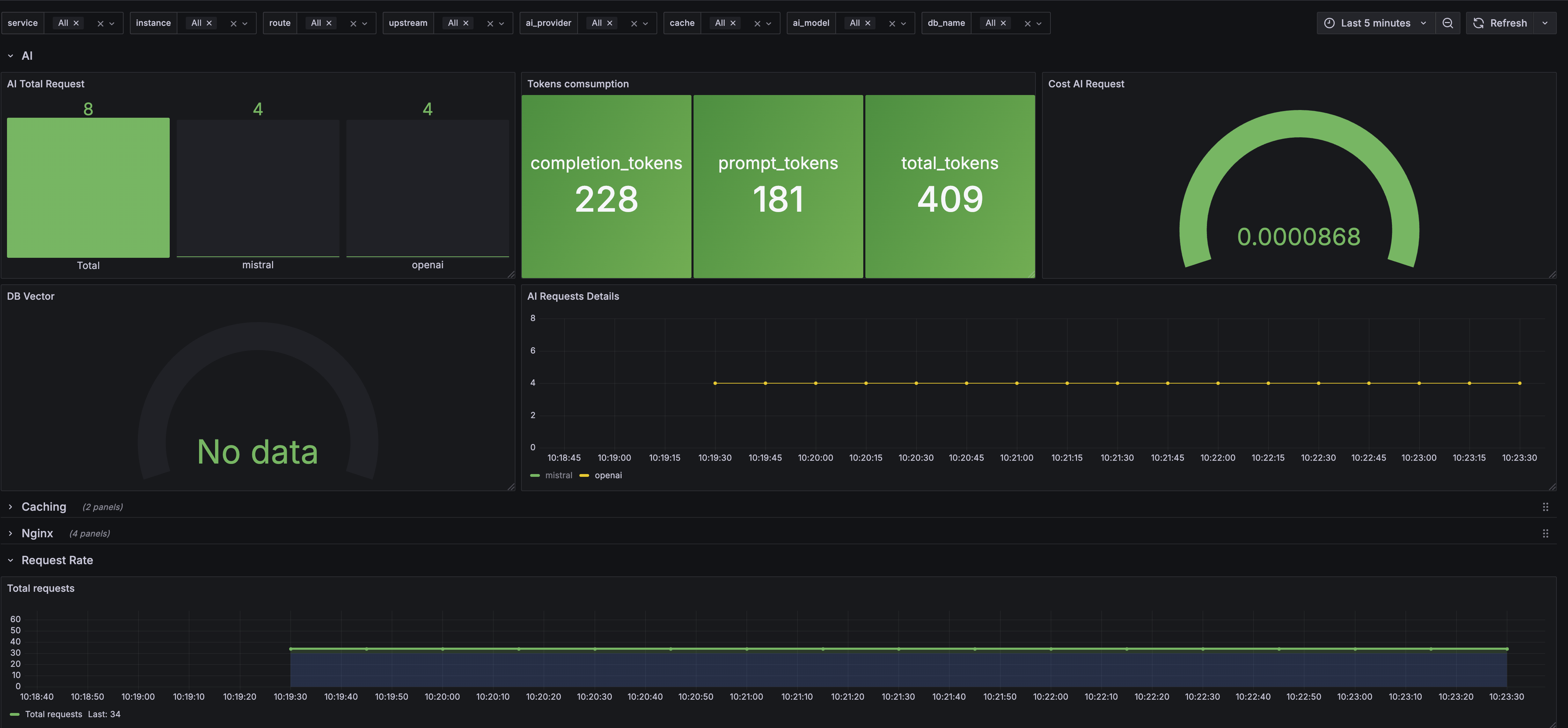
- You should see the following:
- AI Total Request: Total request count and breakdown by provider.
-
Tokens consumption: Counts for
completion_tokens,prompt_tokens, andtotal_tokens. -
Cost AI Request: Estimated cost of AI requests (shown if
input_costsandoutput_costsare configured). -
DB Vector: Vector database request metrics (shown if
vector_dbis enabled). - AI Requests Details: Timeline of recent AI requests.
The visualized metrics in Grafana will look similar to this example dashboard:
Cleanup
Clean up Konnect environment
If you created a new control plane and want to conserve your free trial credits or avoid unnecessary charges, delete the new control plane used in this tutorial.
Destroy the Kong Gateway container
curl -Ls https://get.konghq.com/quickstart | bash -s -- -d